Q-Exchange Blog

537 Installment Sale Trust vs. 1031 Exchange
537 Installment Sale Trust vs. 1031 Exchange: A Comparative Analysis
Introduction
Real estate investors often seek tax-efficient strategies when selling appreciated properties. Two popular approaches are 537 Installment Sale Trusts (537 ISTs) and 1031 Exchanges. Each has distinct tax advantages, liquidity considerations, and reinvestment requirements. This article provides a deep dive into both, using real-world investor case studies to highlight when one is preferable over the other.
Understanding Each Strategy
What is a 537 Installment Sale Trust (537 IST)?
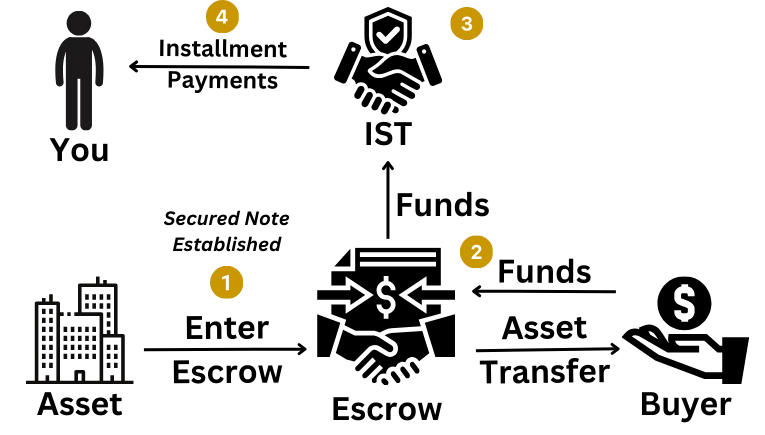
A 537 Installment Sale Trust (IST) allows a seller to defer capital gains tax by selling their property in installments through a third-party trust. This strategy provides tax deferral, investment flexibility, and estate planning benefits. It is structured under IRC Section 453, which governs installment sales.
Key Features:
✅ Tax deferral via installment payments
✅ Greater investment flexibility (stocks, bonds, REITs, private lending, etc.)
✅ Allows diversification beyond real estate
✅ Can be structured to minimize estate tax impact
What is a 1031 Exchange?
A 1031 Exchange, under IRC Section 1031, enables investors to defer capital gains taxes by reinvesting proceeds from a property sale into a like-kind property. This strategy is widely used for portfolio growth and tax efficiency.
Key Features:
✅ Tax deferral by reinvesting in another real estate asset
✅ Strict 45-day identification & 180-day closing deadlines
✅ Requires qualified intermediary to facilitate transactions
✅ Allows for perpetual tax deferral (via successive exchanges)
Pros and Cons of Each Strategy
537 Installment Sale Trust (IST) – Pros & Cons
✅ Pros:
Capital gains tax is deferred as payments are received over time.
Allows investment in diverse asset classes (stocks, bonds, REITs, real estate, etc.).
Provides structured cash flow, improving liquidity.
Can be structured to reduce estate tax liability and benefit heirs.
Existing debt can be paid off without strict reinvestment requirements.
Investors have greater control over reinvestments and cash flow timing.
❌ Cons:
Requires expert tax and legal advisors to structure properly.
Less common, so fewer professionals specialize in ISTs.
1031 Exchange – Pros & Cons
✅ Pros:
Capital gains tax is fully deferred if reinvestment occurs.
Allows for perpetual tax deferral through successive exchanges.
Provides long-term real estate wealth growth through compounding appreciation.
Property can be passed down tax-free with a stepped-up basis.
❌ Cons:
Must reinvest only in real estate (limited flexibility).
Strict IRS deadlines (45-day identification, 180-day closing).
Debt from the sold property must be replaced with equal or greater debt.
Requires a qualified intermediary to handle the transaction.
Investor Case Studies
Case Study #1: High Net Worth Investor Exiting Real Estate
Investor Profile:
Owns a $3M commercial building
Wants to retire and avoid managing properties
Wants predictable cash flow & diversification
537 IST Solution:
The investor sells the property and defers $600K in capital gains taxes.
The proceeds are invested in a diversified portfolio (REITs, annuities, bonds), generating a 5% annual return.
Receives $150K annually in installment payments.
Why Not 1031?
The investor does not want another property or the hassle of real estate management.
Case Study #2: Real Estate Developer Expanding Portfolio
Investor Profile:
Owns a $5M apartment complex
Wants to upgrade to a larger $8M multifamily property
Prefers 100% tax deferral & real estate-only reinvestment
1031 Exchange Solution:
The investor defers $1M in capital gains taxes by reinvesting into the larger property.
Maintains tax-free compounding growth by continually exchanging assets.
Uses a qualified intermediary to facilitate the exchange within IRS deadlines.
Why Not 537 IST?
The investor wants to stay in real estate and continue growing their portfolio.
Financial Projections: 537 IST vs. 1031 Exchange
Scenario: Sale of a $2M Property with a $1M Gain
Capital Gains Tax Rate: 20% Federal + 5% State
Alternative Investments Return (537 IST): 5%
Rental Yield (1031 Exchange): 6%
537 Installment Sale Trust (IST) Outcomes:
Tax Owed Immediately: $0 (deferred)
Reinvestable Amount: Varies (structured payouts)
Annual Cash Flow: $100,000 (5% return on installment investments)
Liquidity: High (structured cash flow)
Long-Term Growth: Dependent on investment strategy
1031 Exchange Outcomes:
Tax Owed Immediately: $0 (deferred)
Reinvestable Amount: $2,000,000
Annual Cash Flow: $120,000 (6% rental yield)
Liquidity: Low (all tied in property)
Which Strategy is Right for You?
✅ Choose 537 IST if:
You want liquidity & diversification beyond real estate.
You are retiring or exiting real estate investments.
You need predictable cash flow and want to reduce estate tax impact.
✅ Choose 1031 Exchange if:
You want to reinvest in real estate and compound wealth.
You plan to continue property ownership and growth.
You can adhere to strict 1031 deadlines.
Conclusion
Both 537 Installment Sale Trusts and 1031 Exchanges offer significant tax advantages for real estate investors. The right choice depends on your financial goals—whether you prioritize liquidity and flexibility (537 IST) or real estate wealth compounding (1031 Exchange). Consulting with a tax advisor can help determine the best approach based on your investment horizon, estate planning goals, and risk tolerance.
Would you like a customized financial projection for your specific real estate portfolio? Let us know, and we can tailor an analysis for your scenario. - Fill out our comparison analysis here: https://www.q-1031.com/revenue-estimator
Ready to Start your Tax-Deferral Journey?
Schedule a 15-minute phone call for further questions or getting started.
Nothing on this site should be interpreted to state or imply that past results are an indication of future performance. This site does not constitute a complete description of our investment services and is for informational purposes only. It is in no way a solicitation or an offer to sell insurance, annuities, securities or investment advisory services except, where applicable, in states where we are registered or where an exemption or exclusion from such registration or licensing exists. Information throughout this internet site, whether stock quotes, charts, articles, or any other statements regarding market or other financial information, is obtained from sources which we, and our suppliers believe reliable, but we do not warrant or guarantee the timeliness or accuracy of this information. Neither our information providers nor we shall be liable for any errors or inaccuracies, regardless of cause, or the lack of timeliness of, or for any delay or interruption in the transmission thereof to the user. All investments involve risk, including foreign currency exchange rates, political risks, different methods of accounting and financial reporting, and foreign taxes.